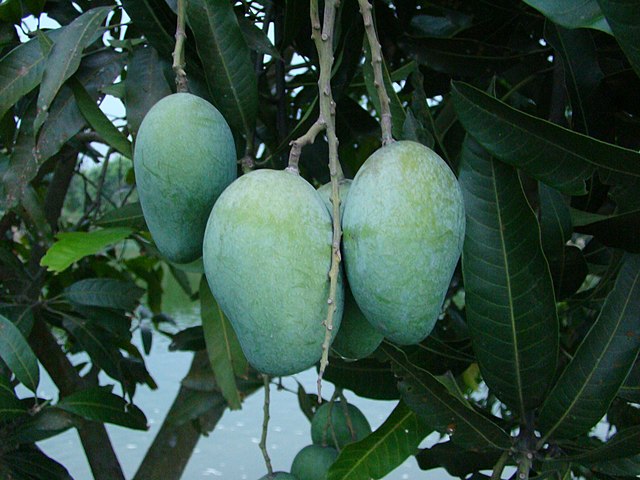
Mango
Mango is the vernacular name commonly applied to the tall, evergreen trees of the species Mangifera indica L. (Anacardiaceae), as well as to their fruit. Mangoes, being sensitive to cool weather, grown in tropical and subtropical regions up to 600 m above sea level.
There are two main groups of cultivars, Indian and Philippine. The former, which are more prevalent, are mono-embryonic and must be grafted. They bear high-quality fruit that has a comparatively long shelf life; its main varieties include Tommy Atkins, Keitt and Kent. The Philippine cultivars are poly-embryonic, require no grafting, and are seldom grown in Israel (except as stocks for grafting).
Mango trees blossom in the spring, the fruit develops through summer, and is picked from late summer to autumn. The fruit is globose or kidney-shaped, with a smooth, thin skin that is green to yellow and red, the edible pulp is fleshy and juicy, usually sweet and the single stone is large. It is eaten fresh, canned or used for juice and jams.
Total, annual, world-wide fruit yield came to about 26 million tons in the year 2002, of which more than half were from India. Brazil, Mexico, Pakistan and The Philippines are also major producers. About 1,700 hectares are planted to mangoes in Israel and about 1,000 tons of fresh fruit are annually exported to Europe. Research on mango biotechnology, breeding, processing, production and protection is summed up by periodical international symposia (e.g. http://www.actahort.org/books/645/).
Major Mango pests in the Middle East
References
Anonymous, 2003. FAO Production Yearbook for 2002, #56. FAO, Rome, Italy.
Anonymous, 2003. Statistical Abstract of Israel, #54. Central Bureau of Statistics, Jerusalem.
Bakr, R.F.A., Badawy, R.M., Mousa, S.F., Hamooda, L.s. and Atteia, S.A. 2009. Ecological and taxonomic studies on the scale insects that infest mango trees at Qaliobiya governorate. Egyptian Acadedy Journal of Biological Sciences 2: 69-89.
Homsky, S. 1989. Mango Growing. Israel Ministry of Agriculture, Department of Fruit Growing and Fruit Board of Israel (in Hebrew).
Kostermans, A.J.G.H. and Bompard, J.-M. 1993. The Mangoes, Their Botany, Nomenclature, Horticulture and Utilization. Academic Press, San Diego.
Pinto, A.C.Q., Pereira, M.E.C. and Alves, R.E. (Eds.) 2004. Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Mango. Acta Horticulturae 645.
Siddiq, M., Brecht, J.E. Sidhu, J.S. (Eds) 2017. Handbook of Mango Fruit: Production, Postharvest Science, Processing Technology and Nutrition. Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 320.
Swirski, E., Wysoki, M. and Izhar, Y. 2002. Subtropical Fruits Pests in Israel. Fruit Board of Israel (in Hebrew with and English Summary).
Websites: