Didesmococcus unifasciatus (Archangelskaya)
Systematic position: Insecta, Hemimetabola, Hemiptera, Sternorrhyncha, Coccomorpha, Coccoidea, Coccidae.
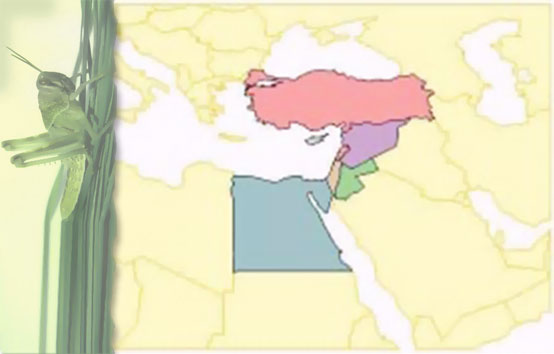
Geographical distribution: Eastern to southern Asia, from Lebanon to China.
Host plants: Didesmococcus unifasciatus has been recorded from various Rosaceae, including Amygdalus, Malus, Prunus and from Ficus and Ulmus.
Morphology: The females are large, globular, about 5 mm in height, dark red in color.
Life history: This pest is univoltine. Females lay several thousand eggs during spring. The emerging crawlers feed for several weeks and enter a summer diapause. In autumn they molt and the nymphs settle in dense colonies on tree twigs. After feeding for a while they undergo a second (winter} diapause, which lasts till next spring.
Economic importance: A minor pest of almond and peach. The main damage is due to much sucking of tree sap and possibly also to its toxic saliva. Heavily infested trees may die within a few years.
Management:
Chemical control: Systemic organophosphates control the pest.
Biological control: Some Aphelinidae and Encyrtidae (including Metaphycus) attack the pest, as well as Chilocorus bipustulatus and several predatory Lepidoptera. These natural enemies usually control the pest, unless disrupted by pesticides.
References
Bolu, H. 2012. A new pest on almond tree, the soft scale Didesmococcus unifasciatus (Archangelskaya) (Hemiptera: Coccidae) and its new records parasitoids, Turkey. Journal of the Entomological Research Society 14: 107-114
Davoodi, A., Talebi, A.A., Fathipour, Y., Daneshvar, S. and Radjabi, G. 2004. Study on the morphological features of four new species of scale insects parasitoids (Hym.: Chalcidoidea) from Iraq.. Agricultural Science (Tabriz) 14: 51-66.
Pfeiffer, D.G. 1997. Deciduous fruit trees. In Ben-Dov, Y. and Hodgson, C.J. (eds) Soft Scale Insects, Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control .Elsevier, Amsterdam. Pp. 293-322.
Talhouk, A.S. 1978. Contributions to the knowledge of almond pests in East-Mediterranean countries. VIII. The establishment of an integrated program of almond pest management in Lebanon. Journal of Applied Entomology 87: 1-14.